The tornado which tore through Stalybridge last night was caused by a supercell thunderstorm. The localised tornado was similar to the one in the Wizard of Oz according to weather experts.
A supercell is a thunderstorm with a deep, persistently rotating updraft also known as rotating thunderstorms.
Of the four classifications of thunderstorms, supercells are the least common and have the potential to be the most severe.
They most commonly occur on the Great Plains of the United States in an area known as Tornado Alley.
One was featured in the Hollywood classic movie The Wizard of Oz.
Tornadoes are vertical funnels of rapidly spinning air. They often come from supercells - large thunderstorms with winds that are already in rotation. According to National Geographic, around one in a thousand storms becomes a supercell, and one in five or six supercells spawns off a tornado.
A tornado forms when warm, humid air collides with cold, dry air. The denser cold air is pushed over the warm air, usually producing thunderstorms. The warm air rises through the colder air, causing an updraft.

If winds vary sharply in speed or direction, that updraft starts to rotate, called a mesocycle. As that mesocycle draws in more warm air from the moving thunderstorm, its rotation speed increases and water droplets from its moist air form a funnel cloud which continues to grow and eventually drops down from the cloud to touch the ground - at which point it becomes classified as a tornado.
The tornado then moves across the surface causing severe damage or destruction to objects in its path.
Around 30 tornadoes a year are reported in the UK, according to the Met Office, which are typically small and short-lived, but can cause structural damage if they pass over built-up areas
The most recent tornado in the UK was in Birmingham in July 2005, measuring T6 on the TORRO scale, causing £40m of damage - reportedly the costliest tornado if not the strongest. A tornado that hit Gunnersbury in London in 1954 was stronger, measuring T7 on the scale.

 A guide to spring bulbs aftercare.
A guide to spring bulbs aftercare.
 ‘I was running a hair salon aged 18 – then I became a walking zombie’
‘I was running a hair salon aged 18 – then I became a walking zombie’
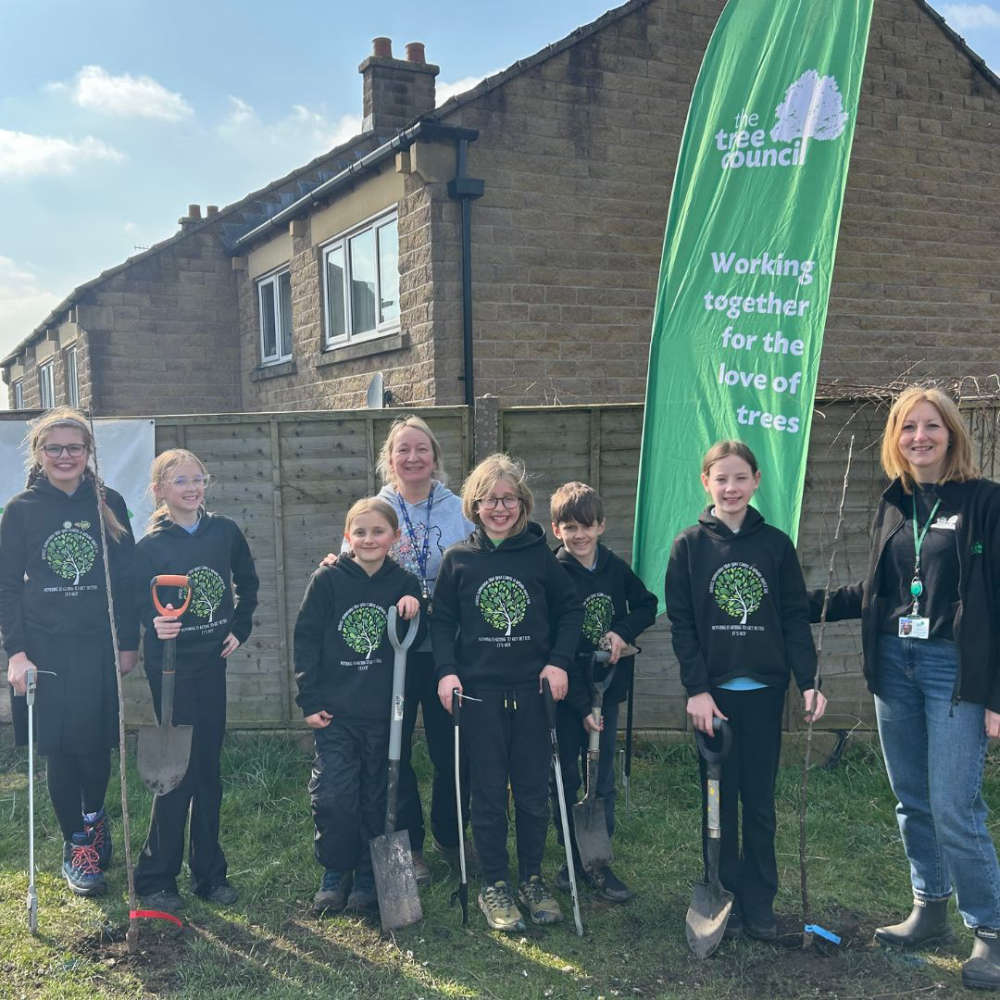 Young Tree Ambassadors plant a legacy on Roughfields
Young Tree Ambassadors plant a legacy on Roughfields
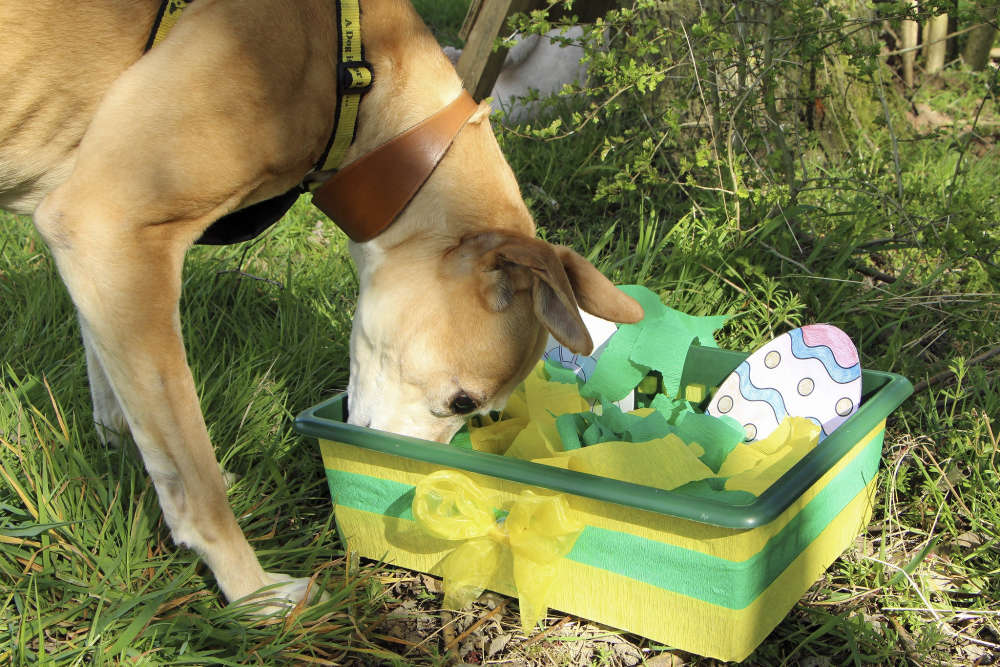 Dogs Trust Manchester gives cracking advice on how to have a dog-friendly Easter
Dogs Trust Manchester gives cracking advice on how to have a dog-friendly Easter